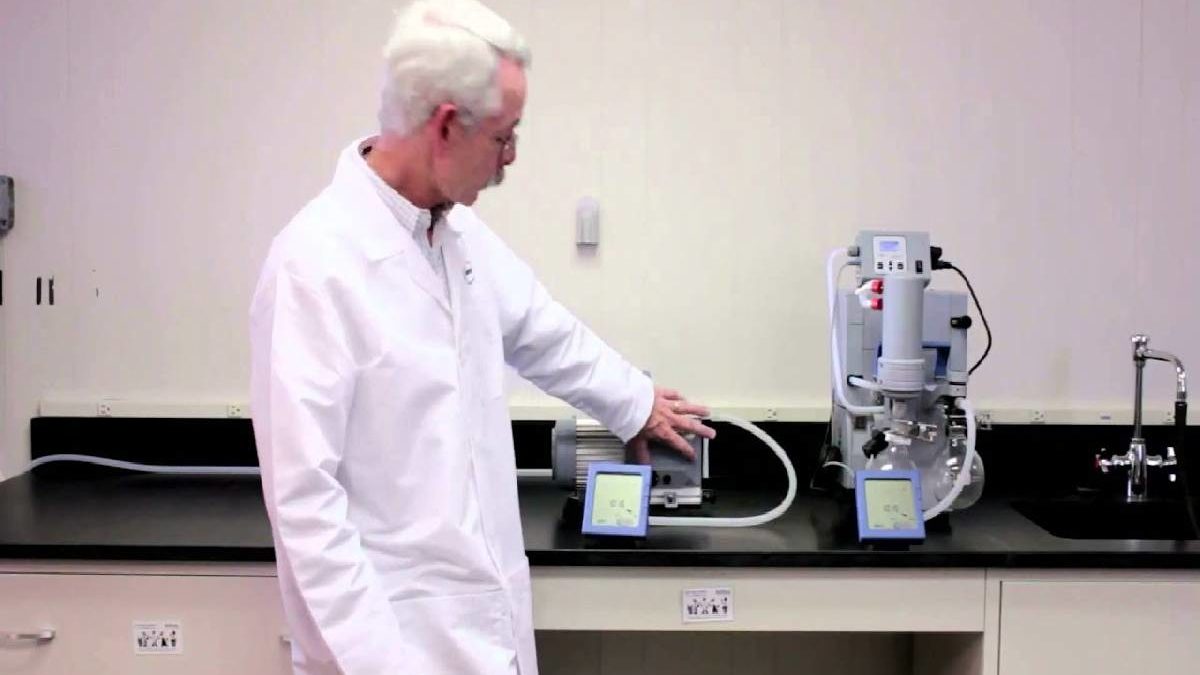
The vacuum pump is used to remove all of the gas molecules in a sealed container or room. There are many vacuum pumps available on the market that you can use in your laboratory.
The equipment is not only used in laboratories, but also with electric lamps and semiconductors. A laboratory pump, for example, will be used to control the evaporation, remove the excess moisture from the room, reduce vapor pressure and filter or aspirate liquid.
Data shows that the vacuum pump market is expected to grow at a compounded annual rate of 6%, from $4.4 billion in 2018 to the estimated $5.5 billion by 2022. This growth can be attributed to the constant demand for semiconductors in the global market. China and Japan are still the dominant manufacturers.
Buyers’ Guide for Laboratory Vacuum Pump
Function should be determined by the objective. The type of vacuum pump you buy should be based on the requirements of your laboratory.
There are four main types of vacuum pumps: lyophilization, freeze-drying or freezing, concentration and evaporation.
Diaphragm
This type of Vacuum Pump can be used for concentration or evaporation. The equipment is too shallow to be suitable for lyophilization. The dry pump uses a pulsing action that closes and open valves to trigger the air flow. You do not require oil to move the parts. It is less susceptible to damage because it doesn’t require oil. It’s also resistant to vapor, chemical and corrosion. This makes it a great tool for dealing with acids and solvents that are corrosive.
Scroll
This is another dry pump type that uses dual spiral scrolls to compress vapor and air, before channeling them towards the exhaust. It is less susceptible to damage, and requires little maintenance. However, it is more expensive than a diaphragm. The scrolls must be changed every 40,000 hours. It’s designed to freeze-dry. It does not perform as well when used with acid. You should only use it on materials that contain less than 20% of acid.
Rotary Vane
The machine is also smaller and more affordable than other vacuum pumps. The rotary vane has a lot of flexibility. It can be used in a variety of applications. Oil is required to lubricate the mechanism’s components. Condensers may be needed to collect vapors and prevent them from entering the pump. This can cause damage. The rotary vane is a high-maintenance pump, which requires you to change and check the oil every 3,500 hours.
Hybrid
This laboratory vacuum pump combines the diaphragm with the rotary vane. The diaphragm acts as a gate for maintaining negative pressure in the oil of the rotary vane. The vapors will be eliminated and the oil condensed. You can replace the oil more frequently than with a standard rotary vane. The hybrid pump can be used to freeze-dry.
The vacuum pumps used in labs around the globe are all common types. The cost will vary depending on the brand, capacity, and features.
Helpful Resources
1. Top 10 Commandments for the Long Distance Runner
2. Pilates exercises to do at home
3. Best Chest Exercises For Building Muscles
4. 16 Best Running Shoe [2020] for Neutral Runners
5. The best abdominal exercises to improve your abdomen
Health & Wellness
Five Simple Ways to Get Rid of Bloating
Entertainment, Health & Wellness
7 Quick Tips to Stay Active With a Disability